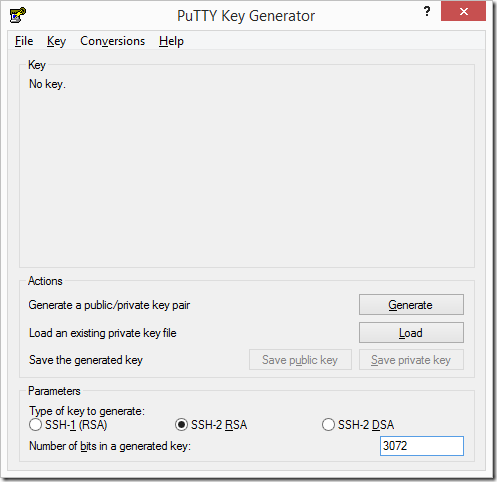
Aug 09, 2018 Generate SSH Keys on Windows 10 with PuTTY. To generate a key pair with the PuTTY key generator, simply run andputtygen.exe click the Generate button in the window that appears. You will be asked to move the mouse and press keys to improve the random number generation at the heart of SSH security.
How do I regenerate OpenSSH sshd server host keys stored in /etc/ssh/ssh_host_* files? Can I safely regenerate ssh host keys using remote ssh session as my existing ssh connections shouldn’t be interrupted on Debian or Ubuntu Linux? How do I regenerate new ssh server keys? How to regenerate new host keys on a Debian or Ubuntu Linux?May 05, 2014 Install putty and generate ssh key to auto log in to Ubuntu server 14 Table of contents: 1. Install putty and generate ssh key to auto log in to Ubuntu server 14 Table of contents: 1. While not required, the SSH private key can be encrypted with a passphrase for added security. The PuTTY SSH client for Microsoft Windows does not share the same key format as the OpenSSH client. Therefore, it is necessary to create a new SSH public and private key using the PuTTYgen tool or convert an existing OpenSSH private key. How do I install an SSH private key generated by PuTTYgen? Ask Question Asked 9 years. Then you can create you own ssh key-pair using ssh-keygen and copy the new public key to the. But I stumbled upon a similar problem with Windows 10 anniversary edition which now support Ubuntu kernel. I use to use Putty before for connecting to Linux. Puttygen on Linux - SSH Key Generator. This page is about PuTTYgen on Linux. It is rarely necessary to export a private key from PuTTY to Tectia SSH or OpenSSH. However, the process is described here, as it can sometimes be necessary when, for example, an application is moved to Linux in the cloud and the destination server of a file.
[donotprint][/donotprint]To regenerate keys you need to delete old files and reconfigure openssh-server. It is also safe to run following commands over remote ssh based sessionJul 29, 2019 Establishing an SSH (Secure Shell) connection is essential to log in and effectively manage a remote server. Encrypted keys are a set of access credentials used to establish a secure connection. This guide will walk you how to generate SSH keys on Ubuntu 18.04. Go to Windows Start menu → All Programs → PuTTY → PuTTYgen. Creating a new key pair for authentication. To create a new key pair, select the type of key to generate from the bottom of the screen (using SSH-2 RSA with 2048 bit key size is good for most people; another good well-known alternative is ECDSA).
. Your existing session shouldn’t be interrupted.Why regenerate new ssh server keys?
Most Linux and Unix distribution create ssh keys for you during the installation of the OpenSSH server package. But it may be useful to be able re-generate new server keys from time to time. For example, when you duplicate VM (KVM or container) which contains an installed ssh package and you need to use different keys from cloned KVM VM guest/machine.
Steps to regenerate OpenSSH host keys on Linux
Let us see all steps
Step 1 – Delete old ssh host keys
Login as the root and type the following command to delete files on your SSHD server:# /bin/rm -v /etc/ssh/ssh_host_*
Sample outputs:
Step 2 – Debian or Ubuntu Linux Regenerate OpenSSH Host Keys
Now create a new set of keys on your SSHD server, enter:# dpkg-reconfigure openssh-server
Sample output:
You just regenerated new ssh server keys. You need to restart ssh server:$ sudo systemctl restart ssh
OR$ /etc/init.d/ssh restart
Step 3 – Update all ssh client(s) known_hosts files
Finally, you need to update ~/.ssh/known_hosts files on client computers, otherwise everyone will see an error message that read as follows:
Either remove host fingerprint or update the file using vi text editor (command must be typed on client machine):$ ssh-keygen -R remote-server-name-here
Now login using the ssh command:$ ssh vivek@server1.cyberciti.biz
Conclusion
You just regenerated OpenSSH Host Keys on a Debian or Ubuntu Linux using the dpkg-reconfigure command. For more info see the man page or this wiki page here:$ man dpkg-reconfigure
$ man sshd
ADVERTISEMENTS
Introduction
Establishing an SSH (Secure Shell) connection is essential to log in and effectively manage a remote server. Encrypted keys are a set of access credentials used to establish a secure connection.
This guide will walk you how to generate SSH keys on Ubuntu 18.04. We will also cover setting up SSH key-based authentication to connect to a remote server without requiring a password.
- A server running Ubuntu 18.04
- A user account with sudo privileges
- Access to a terminal window / command line (Ctrl-Alt-T)
If you are already running an Ubuntu 18.04 server, you can skip this step. If you are configuring your server for the first time, you may not have SSH installed.
1. Start by installing the tasksel package:
The system will first ask for confirmation before proceeding:
2. Next, use tasksel to install the ssh-server:
3. Load the SSH server service, and set it to launch at boot:
On your client system – the one you’re using to connect to the server – you need to create a pair of key codes.
To generate a pair of SSH key codes, enter the commands:
This will create a hidden directory to store your SSH keys, and modify the permissions for that directory. The ssh-keygen command creates a 2048-bit RSA key pair.
For extra security, use RSA4096:
If you’ve already generated a key pair, this will prompt to overwrite them, and those old keys will not work anymore.
The system will ask you to create a passphrase as an added layer of security. Input a memorable passphrase, and press Enter.
This process creates two keys. One is a public key, which you can hand out to anyone – in this case, you’ll save it to the server. The other one is a private key, which you will need to keep secure. The secure private key ensures that you are the only person who can encrypt the data that is decrypted by the public key.
Step 2- Copy Public Key to the Ubuntu Server
First, get the IP address of the Ubuntu server you want to connect to.
In a terminal window, enter:
The system’s IP address is listed in the second entry:
On the client system, use the ssh-copy-id command to copy the identity information to the Ubuntu server:
Replace server_IP with the actual IP address of your server.
If this is the first time you’re connecting to the server, you may see a message that the authenticity of the host cannot be established:
Type yes and press Enter.
The system will check your client system for the id_rsa.pub key that was previously generated. Then it will prompt you to enter the password for the server user account. Type it in (the system won’t display the password), and press Enter.
The system will copy the contents of the ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub from the client system into the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys directory of the server system.
The system should display:
If your system does not have the ssh-copy-id command, you can copy the key manually over the SSH.
Use the following command:
To log in to a remote server, input the command:
The system should not ask for a password as it is negotiating a secure connection using the SSH keys. If you used a security passphrase, you would be prompted to enter it. After you do so, you are logged in.
If this is the first time you’ve logged into the server, you may see a message similar to the one in part two. It will ask if you are sure you want to connect – type yes and press Enter.
Putty Generate Ssh Key For Ubuntu Windows 10
Step 4- Disable Password Authentication
Generate Ssh Key With Putty
This step creates an added layer of security. If you’re the only person logging into the server, you can disable the password. The server will only accept a login with your private key to match the stored public key.

Edit the sshd_config file:
Search the file and find the PasswordAuthentication option.
Edit the file and change the value to no:
Save the file and exit, then restart the SSH service:
Verify that SSH is still working, before ending the session:
If everything works, you can close out and resume work normally.
By following the instructions in this tutorial, you have setup SSH-key-based authentication on an Ubuntu 18.04 server.
The connection is now highly secure as it uses a set of unique, encrypted SSH keys.
Next you should also read
Learn how to set up SSH key authentication on CentOS to safely communicate with remote servers. Create the…
When establishing a remote connection between a client and a server, a primary concern is ensuring a secure…
Nginx is an open-source server utility designed to work as a reverse proxy, intercepting client requests and…
Putty Use Ssh Key
In this tutorial, Find out How To Use SSH to Connect to a Remote Server in Linux or Windows. Get started with…